what happens in the prophase of mitosis Prophase mitosis meiosis khan profase tahapan chromosomes interphase phases kompas tahap chromosome abnormal biologi penting uas microbenotes appropriate clipartkey fases
Mitosis and meiosis are two crucial processes for the growth and reproduction of cells in organisms. Both of these processes involve cell division, where one cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Among the different phases of cell division, prophase is one of the most significant phases. During prophase, the chromatin fibers in the nucleus start to condense and become visible under a microscope. As they condense, they form discrete structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids, held together at the centromere. The nucleolus disappears, and the nuclear envelope breaks down, leading to the release of chromosomes into the cytoplasm. There are two types of prophase - prophase I and prophase II. Prophase I occurs during meiosis, where homologous chromosomes synapse, a process called “crossing over” occurs, and genetic recombination takes place. The result is a genetically diverse pool of daughter cells. On the other hand, prophase II occurs in the second cell division of meiosis and mitosis, where the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. In both types of prophase, spindle fibers, which consist of microtubules, start to form at opposite poles of the cell. These spindle fibers capture the chromosomes at their centromeres and align them at the center of the cell, forming the metaphase plate. The spindle fibers then pull the sister chromatids apart, separating them into individual chromosomes. This separation of chromosomes is essential in the process of cell division as each daughter cell needs to have an identical set of chromosomes. Any mistake in this segregation can lead to chromosomal abnormalities and diseases. In conclusion, prophase is a crucial phase of cell division, where chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear envelope breaks down, spindle fibers form, and chromosomes align at the cell’s center. These events ultimately lead to the separation of sister chromatids and the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells. Understanding the finer details of prophase can provide a greater insight into the processes of meiosis, mitosis, and cell division, which are vital for the survival and growth of all organisms.
If you are looking for The Steps of Mitosis | Biology for Majors I you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Images about The Steps of Mitosis | Biology for Majors I like Stages of the Cell Cycle - Mitosis (Interphase and Prophase) | Owlcation, Prophase in mitosis and meiosis (Prophase 1 and 2) and also Stages of the Cell Cycle - Mitosis (Interphase and Prophase) | Owlcation. Read more:
The Steps Of Mitosis | Biology For Majors I
 courses.lumenlearning.comprophase mitosis steps stage cell biology stages micrograph chromosomes first
courses.lumenlearning.comprophase mitosis steps stage cell biology stages micrograph chromosomes first
Prophase In Mitosis And Meiosis (Prophase 1 And 2)
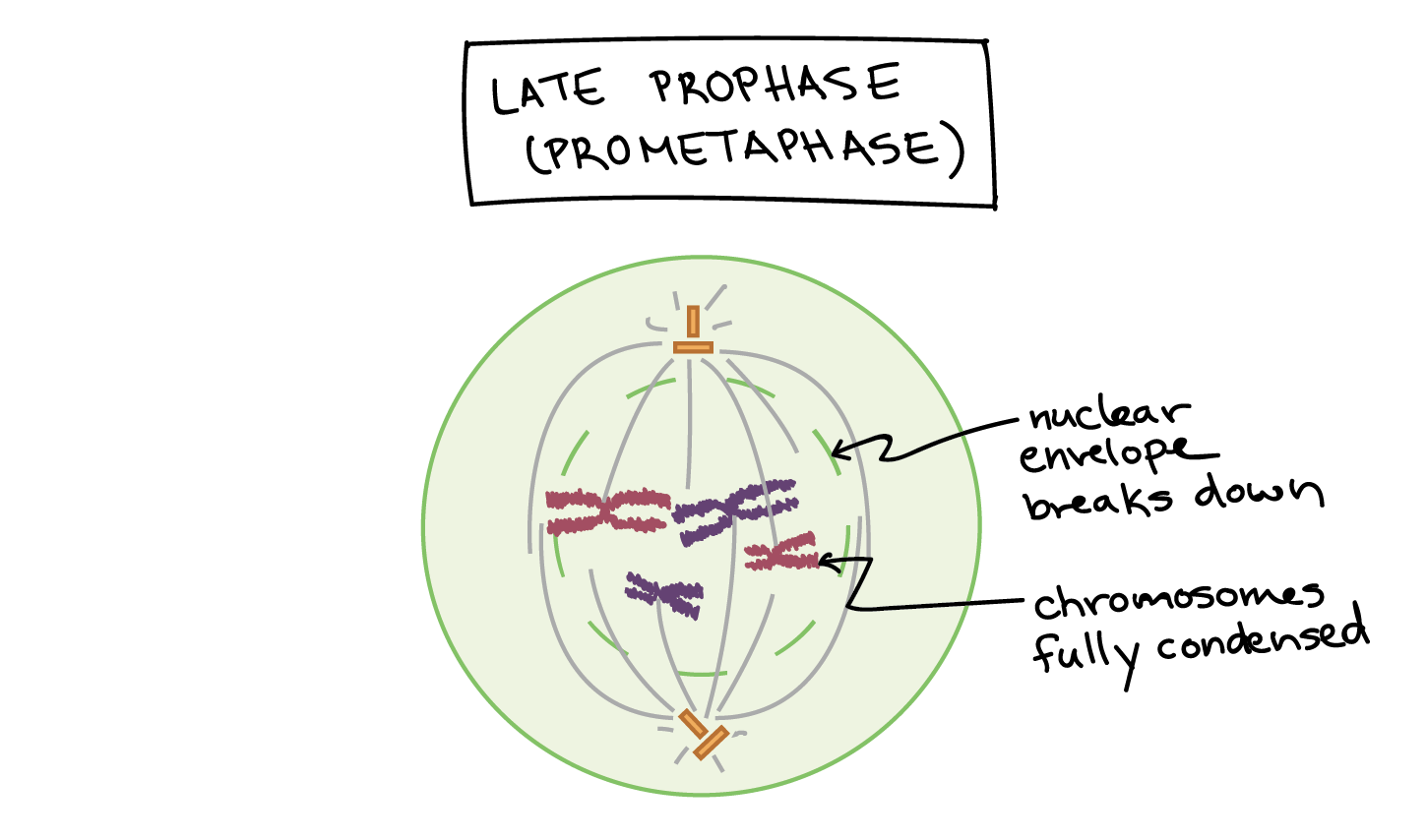 microbenotes.comprophase mitosis meiosis microtubules
microbenotes.comprophase mitosis meiosis microtubules
Prophase In Mitosis And Meiosis (Prophase 1 And 2)
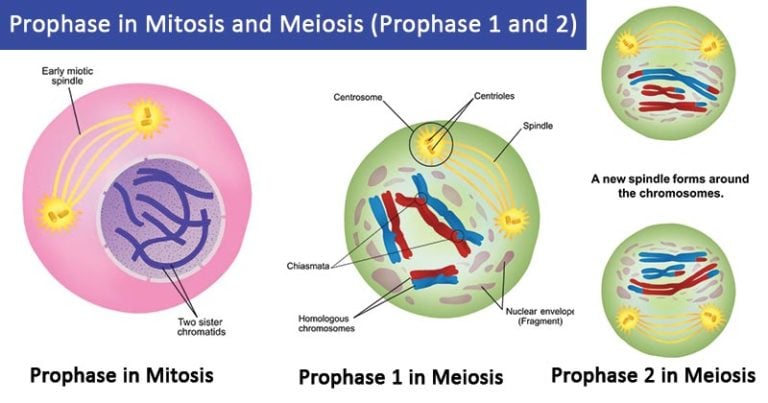 microbenotes.comprophase meiosis mitosis chromatids spindles cells mitotic produced cycle
microbenotes.comprophase meiosis mitosis chromatids spindles cells mitotic produced cycle
31 Label Each Phase Of The Cell Cycle In The Figure Below With The
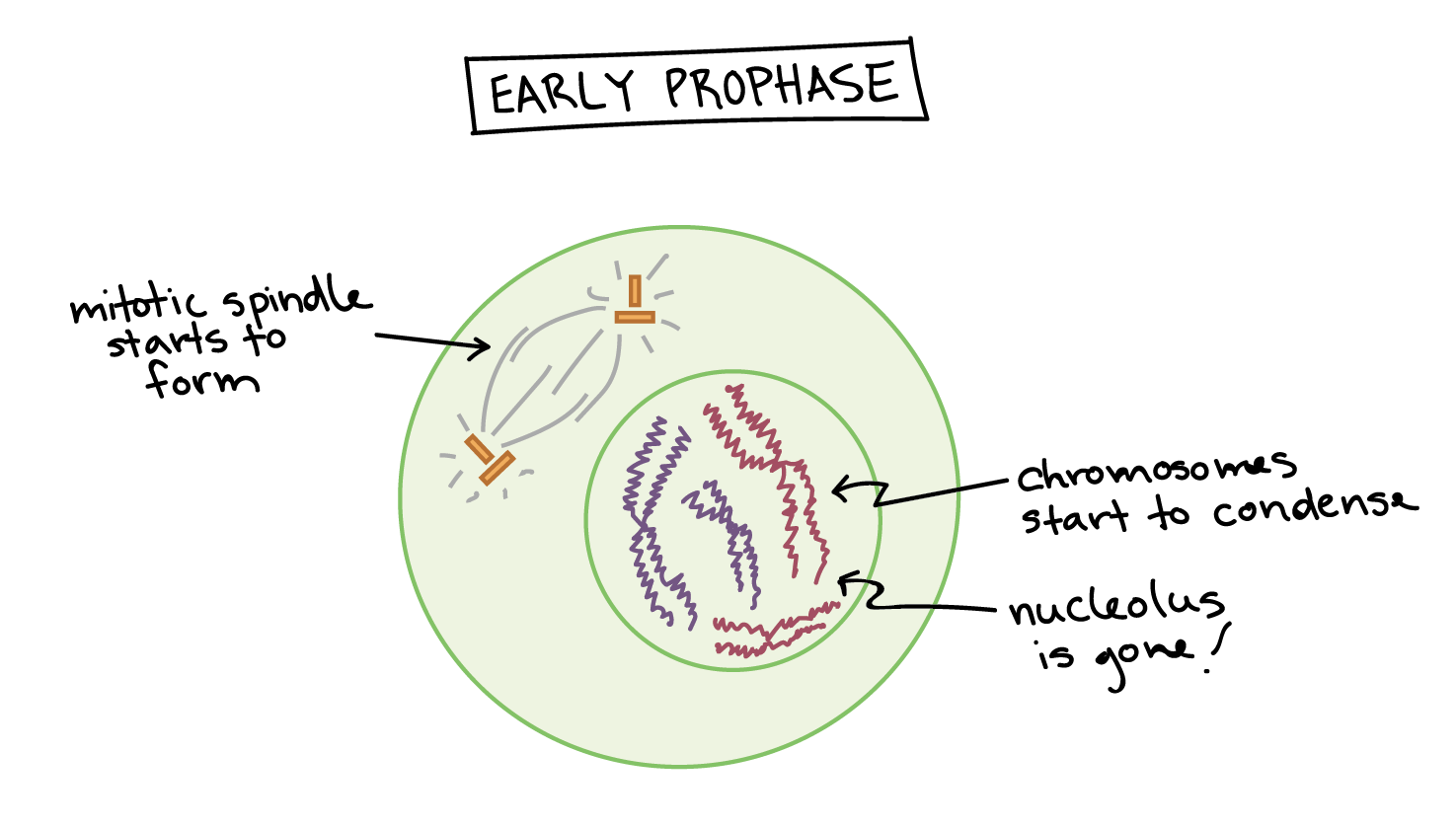 documentdowu.blogspot.comprophase mitosis meiosis khan profase tahapan chromosomes interphase phases kompas tahap chromosome abnormal biologi penting uas microbenotes appropriate clipartkey fases
documentdowu.blogspot.comprophase mitosis meiosis khan profase tahapan chromosomes interphase phases kompas tahap chromosome abnormal biologi penting uas microbenotes appropriate clipartkey fases
Stages Of The Cell Cycle - Mitosis (Interphase And Prophase) | Owlcation
 owlcation.commitosis cell prophase cycle stages interphase stage chromosomes first supercoiling where visible very microscope under apoptosis thanks light
owlcation.commitosis cell prophase cycle stages interphase stage chromosomes first supercoiling where visible very microscope under apoptosis thanks light
Mitosis cell prophase cycle stages interphase stage chromosomes first supercoiling where visible very microscope under apoptosis thanks light. The steps of mitosis. Prophase in mitosis and meiosis (prophase 1 and 2)